The term Diabetic Foot Ulcer encompasses a critical health issue prevalent among individuals with diabetes. This condition involves wounds, typically slow-healing, that occur predominantly on the feet of those who have diabetes. This article aims to provide an in-depth exploration of diabetic foot ulcers, elucidating their causes, potential consequences, and the importance of effective management strategies.
Exploring the Nature of Diabetic Foot Ulcers
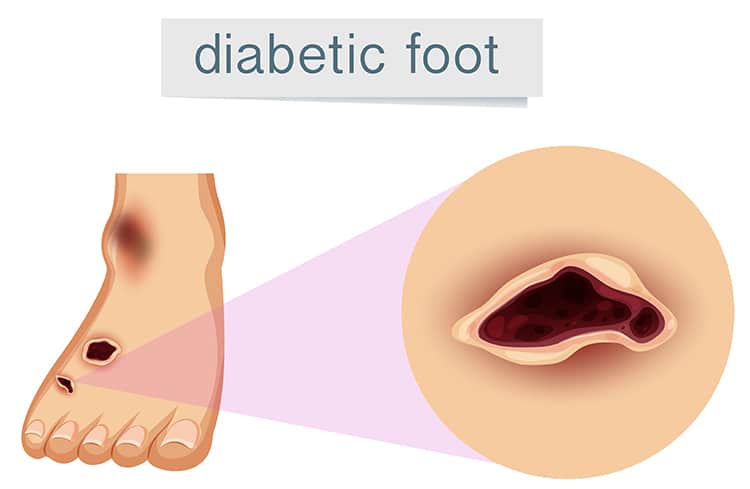
A Diabetic Foot Ulcer is more than just a wound; it’s a complex medical condition often leading to severe health complications such as infections, gangrene, or amputation if neglected. These ulcers directly result from skin tissue deterioration, exposing the underlying layers.
Key Causes and Contributing Factors
Multiple factors influence the development of a diabetic foot ulcer:
Impaired Blood Circulation:
- In diabetics, poor blood circulation, especially in the lower extremities, can hinder wound healing, elevating the risk of ulcer formation.
Neuropathy:
- Diabetes can cause significant nerve damage, leading to a loss of foot sensation. Consequently, minor injuries can go unnoticed and worsen over time.
Foot Deformities and Pressure Points:
- Foot deformities are not uncommon in diabetics and can create areas of increased pressure, eventually causing skin breakdown.
Ineffective Glycemic Control:
High blood sugar levels can adversely affect the body’s natural healing processes, contributing to the severity and persistence of foot ulcers.
Recognizing Symptoms of Diabetic Foot Ulcers
For individuals managing diabetes, the ability to recognize the early symptoms of a Diabetic Foot Ulcer is crucial in preventing severe complications. Key symptoms to be aware of include:
- Signs of Inflammation: The first indication often includes swelling, redness, or a warm sensation in a specific foot area. These signs suggest an inflammatory response, potentially signaling the start of an ulcer.
- Discharge or Unusual Odors: The presence of discharge, or a noticeable, unusual odor emanating from a foot wound, is a clear sign of infection. This discharge can range from clear to yellowish or even greenish in color, depending on the nature and severity of the disease.
- Black Tissue (Eschar): The appearance of black tissue around a wound, known as eschar, indicates necrosis or death of tissue, which is a severe sign. This necrotic tissue can be a precursor to more severe complications and requires immediate medical attention.
- Numbness or Discomfort: Due to neuropathy, individuals may experience numbness, reducing their ability to feel pain or discomfort from a developing ulcer. However, any noticeable discomfort or pain in the feet should not be ignored, as it can indicate underlying problems.
Consequences of Neglecting Ulcers
The consequences of not promptly addressing a Diabetic Foot Ulcer are severe and can lead to life-altering complications:
- Localized or Systemic Infections: If an ulcer is left untreated, it can lead to infections. These infections can be localized to the wound area or, more worryingly, can become systemic, spreading throughout the body. Systemic infections are particularly dangerous and can lead to severe health complications.
- Potential Gangrene: One of the most serious risks associated with untreated diabetic foot ulcers is the development of gangrene. Gangrene occurs when tissue dies due to a lack of blood supply, leading to severe infections that spread to the bone and surrounding tissues.
- Amputation: In extreme cases where ulcers are severely infected and have led to extensive tissue damage, amputation might become necessary. This is often the last resort to prevent the spread of infection and to save the patient’s life. Amputation can have significant physical, emotional, and psychological impacts on a patient’s life.
Understanding and being vigilant about these symptoms and consequences is paramount for individuals with diabetes. Early detection and prompt treatment, including Diabetic Wound Gel, can prevent the progression of ulcers and avoid these severe complications. Regular check-ups with healthcare providers, maintaining good foot hygiene, and controlling blood sugar levels are essential steps in managing the risk of diabetic foot ulcers.
Preventive Measures and Treatment
Preventing Diabetic Foot Ulcers hinges on comprehensive diabetes management. Regular foot examinations and wearing appropriate footwear are essential preventive strategies. In cases where ulcers do develop, prompt treatment is imperative. This includes employing Diabetic Wound Gel for effective wound care, controlling infections, and reducing pressure on the affected area. Advanced treatments may be necessary for severe ulcers.
The Journey of Living with Diabetic Foot Ulcers
Managing a diabetic foot ulcer requires a holistic approach, encompassing diligent wound care, constant infection monitoring, and regular consultations with healthcare professionals. Psychological support is also vital, as chronic wound management can be a significant source of stress.
Embracing Prevention and Proactive Care
Diabetic Foot Ulcers are a complex complication of diabetes, emphasizing the need for thorough diabetes management and awareness. By understanding the risk factors, symptoms, and treatment options, including Diabetic Wound Gel, individuals can better navigate the challenges posed by these ulcers, leading to improved health and quality of life.