Introduction
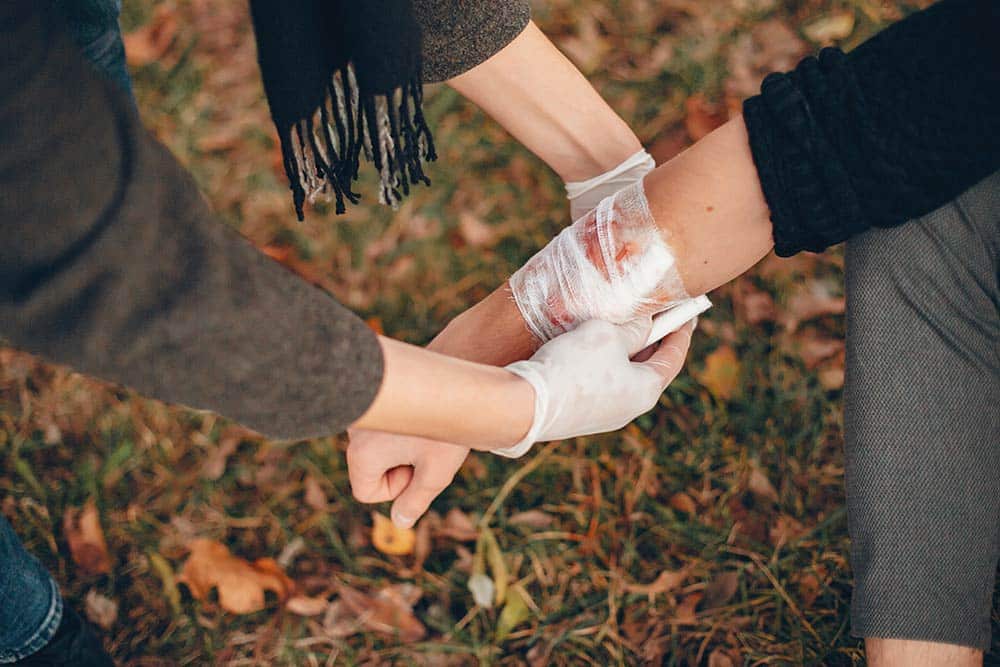
Acute wound management is essential to medical care, dealing with sudden injuries that require immediate attention. These wounds, ranging from minor cuts to severe lacerations, necessitate a systematic approach for effective healing and prevention of complications. This article delves into the various aspects of acute wound management, highlighting the importance of timely and appropriate care.
Understanding Acute Wounds
An acute wound is a sudden injury to the skin, typically resulting from external causes like accidents, surgical incisions, or burns. These wounds disrupt the skin’s integrity and can vary significantly in severity, from superficial scratches to deep, penetrating injuries.
Chronic wounds don’t follow a predictable healing process. They are characterized by slow healing due to underlying conditions, distinguishing them from acute wounds. Employing effective Acute Wound Management techniques is vital to mitigate infection risks, promote efficient healing, and reduce the likelihood of scarring.
Types of Acute Wounds
We can broadly categorize acute wounds into two main types: surgical and traumatic.
- Surgical Wounds: These are incisions purposefully made by healthcare professionals, often with clean, precise cuts. They may be closed using stitches, staples, or adhesives or left open to heal. The risk of infection classifies these wounds further into clean, contaminated, and dirty categories.
- Traumatic Wounds: These result from an injury or force, such as a blow, scratch, or cut. Traumatic wounds include abrasions (caused by a rough surface scraping the skin). Punctures (from a pointed object). Lacerations (tears in the skin from a sharp blow). And incisions (straight-edged cuts by sharp objects).
Healing Process of Acute Wounds
The normal healing process of acute wounds progresses through a series of stages, typically completed within 6-12 weeks. This process involves coagulation and inflammation, followed by tissue growth and remodelling. Most surgical wounds belong to the category of acute wounds, and we expect them to follow these stages of healing.
Principles and Management of Acute Wounds
Effective management of acute wounds is crucial to ensure proper healing and prevent complications like infection or scarring. The process begins with a thorough wound assessment, including depth, size, and contamination potential, guiding treatment based on location and severity.
Key aspects include bleeding control, cleansing, and debridement. Pain management is integral, balancing comfort with the patient’s health status. Dressing choice plays a crucial role, ranging from simple coverings to advanced options like hydrogels or alginates, with modern wound care products like Wound Treatment Gel enhancing healing.

Effective acute wound management involves assessment, bleeding control, cleansing, debridement, pain management, and suitable dressing, with advanced products and techniques crucial for efficient healing and minimizing complications.
Conclusion: Navigating Acute Wound Care
Effective management of acute wounds integrates advanced care techniques with an understanding of each wound’s unique challenges. Removing non-viable tissue through debridement facilitates healing from the wound’s base and often accompanies pain management to ensure patient comfort.
The use of specialized dressings, like hydrocolloids, alginates, or foam, plays a crucial role in maintaining a moist healing environment and adapting to different wound needs. Exploring products such as Wound Treatment Gel can significantly enhance healing effectiveness.
Healthcare providers must navigate the challenges of individual wound care, balancing treatment personalization with vigilance against complications like infection or delayed healing.
In summary, acute wound management is a dynamic field requiring continuous adaptation and embracing advanced products and techniques, such as those detailed in Acute Wound Management. Staying abreast of these developments ensures optimal patient care and effective healing outcomes.